柔性电子产品的快速发展激发了人们对可穿戴应用的极大兴趣,特别是那些将柔性电子产品纳入纺织品的应用。其中,显示功能对于柔性可穿戴电子纺织品尤为重要,因为它可以实时显示来自其他集成器件的信号,增强用户体验和交互。
近日,浙江理工大学纺织科学与工程学院(国际丝绸学院)胡毅教授团队在国际知名期刊Advanced Fiber Materials上(影响因子21.3)在线发表了题为《Fluorescent Dye-Enhanced ACEL Fibers for Omnidirectional Luminescence and Voice-Interactive Human-Machine Interfaces》的研究论文。本研究立足纺织染整领域优势,创新引入荧光染料实现发光纤维色彩调节,并集成声音传感模块,通过识别语音(英文单词/句子)和音量(分贝大小)实现柔性可穿戴纺织品的多色显示。论文DOI:10.1007/s42765-025-00579-w。浙江理工大学纺织科学与工程学院(国际丝绸学院)硕士研究生张英和刘明宇为本文共同第一作者,通讯作者为浙江理工大学博士生导师胡毅教授。

虽然传统的平面和薄膜可穿戴发光电子器件具有很高的光学和电子性能,但通常它们的透气性和舒适性有限,导致不太适合长期穿戴。作为纺织品的基本组成部分,纤维具有优异的柔韧性。当编织到织物结构中时,基于纤维的电子元件可以在不影响透气性的情况下获得更高的耐久性、灵活性和集成度。
鉴于此,浙江理工大学纺织科学与工程学院(国际丝绸学院)博士生导师胡毅教授课题组报道了一种方法,通过结合共轭静电纺丝和溶液浸涂技术连续制备多色彩ACEL纤维器件。通过在纤维器件中引入有机荧光染料作为颜色转换层,实现了宽色域的颜色调制。由此制备的ACEL纤维是智能纺织品应用的理想选择,因为它在保持优异手感的同时显示出明亮、均匀和全向的发光性能。这项工作的创新之处在于将ACEL纤维与具备语音和音量识别功能的声音传感驱动模块集成在一起,从而扩大了其在听障人士通信、高噪声环境预警和医疗呼吸声监测等领域的潜在应用。总体而言,该研究为可穿戴光电系统、交互纺织品和多功能电子纺织平台开辟了新的可能性。
图 1 ACEL纤维声音传感可视化显示系统的设计、制造及集成

Fig. 1 Design, fabrication, and integration of ACEL fiber-based sound-sensing visual display system. a Schematic diagram of the ACEL fiber preparation process, with an inset showing the luminescent spinning solution composition. b Structural representation of the core-multi-shell ACEL fiber, illustrating its functional layers. c Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of the ACEL fiber cross-section, showing the distinct layer structure. d Fluorescence microscopy image of the ACEL fiber cross-section, highlighting the uniform distribution of fluorescent dyes within the color conversion layer. e Example of ACEL fiber integrated into a hand-embroidered “Lion Dance” light-emitting textile pattern. Scale bar, 5 cm. f Luminescent hand-embroidered sentence/word pattern of ACEL fiber used for sound-sensing applications. Scale bar, 5 cm. g A physical image of the sound-sensing EL driver module, designed for speech recognition and volume detection. Scale bar, 1 cm. h Diagram of application scenarios, where the sound sensor captures sound signals to control the light-emitting display of ACEL fibers, facilitating visual barrier-free communication for hearing-impaired individuals.
ACEL纤维的连续制造是通过结合共轭静电纺丝和溶液浸涂技术来实现的。该制备工艺包括六个关键步骤:(I)共轭静电纺丝发光层,(II)浸涂介质层,(III)包缠铜丝外电极,(IV)等离子体表面改性,(V)浸涂银纳米线(AgNWs)外电极,(VI)浸涂封装层。所制备的ACEL纤维的总直径约为855 μm,发光层厚度约为57 μm。
图 2 ACEL纤维的颜色调节特性
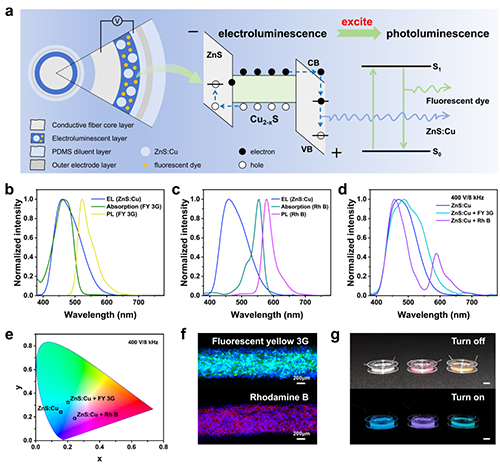
Fig. 2 Color-conditioning properties of ACEL fibers. a Schematic representation of the structure and color-conditioning mechanism of multicolor ACEL fibers. b Absorption and photoluminescence (PL) spectra of the FY 3G dye. c Absorption and PL spectra of Rh B dye. d Comparison of electroluminescence (EL) spectra of ACEL fibers with and without the color conversion layer. e CIE coordinates of ACEL fibers with and without the color conversion layer. f Fluorescence microscopy images of ACEL fibers integrated with FY 3G and Rh B color conversion layers. g Visual representation of ACEL fibers exhibiting different colors. Scale bar, 1 cm.
该工作继团队前期在多色平面柔性ACEL器件的研究基础上,介绍了在原始ACEL纤维的ZnS:Cu/PVDF-HFP发光层上浸涂荧光染液的工艺。该策略通过构建颜色转换层实现多色发射,提高光谱输出。ZnS:Cu/PVDF-HFP复合微纳米纤维的多孔结构使其具有高比表面积,为有机荧光染料分子提供了更多的物理吸附位点,有利于染料分子的物理吸附。这种将荧光染料浸渍在纳米纤维发光层上的方法,有利于多色ACEL纤维的连续生产,为未来连续和批量化生产荧光染料增强多色ACEL纤维提供了新的可能性。
图 3 ACEL纤维的光学性能
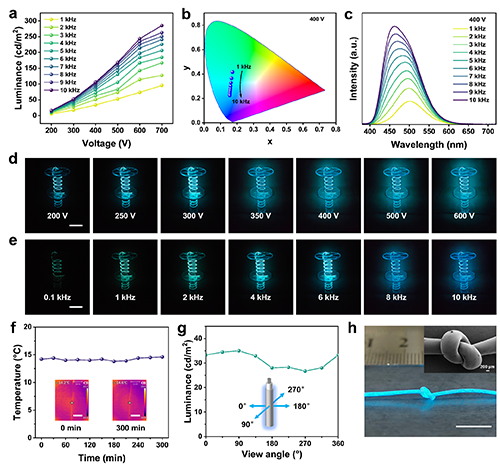
Fig. 3 Performance characteristics of ACEL fibers. a Variation in emitted brightness as a function of applied voltage at driving frequencies. b Change in emitted color coordinates within the CIE 1931 color space with frequency variation (at a fixed voltage of 400 V). The black arrow indicates the shift in color coordinates when the applied frequency increases from 1 kHz to 10 kHz. c Emission spectra of ACEL fibers at different driving frequencies (1-10 kHz) under a fixed voltage of 400 V. d Optical images of ACEL fibers at different applied voltages (with a fixed frequency of 5 kHz). Scale bar, 5 cm. e Optical images of ACEL fibers at different applied frequencies (with a fixed voltage of 300 V). Scale bar, 5 cm. f Temperature variation profiles of ACEL fibers during operation, with the inset showing the corresponding infrared thermography. Scale bar, 0.5 cm. g Dependence of luminescence brightness on the observation angle, with the inset displaying the schematic of the test angle. h ACEL fiber in a knotted configuration, with the inset showing its SEM image. Scale bar, 1 cm.
系统探究了无颜色转换层ACEL纤维在不同驱动电压和频率下的电致发光特性。ACEL纤维的电致发光亮度随交流电压的增加而显著增加。在固定的5 kHz驱动频率下,当驱动电压从200 V增加到700 V时,纤维发光亮度从12.95 cd/m2增大到206.20 cd/m2。此外,增加驱动电压的频率也会显著提高器件的亮度。除了影响发光强度外,驱动频率还会引起ACEL纤维EL光谱的显著偏移。具体来说,在400 V恒定电压下,将频率从1 kHz增加到10 kHz,会导致EL发射峰出现明显的蓝移,从502 nm过渡到462 nm。这种光谱偏移对应了从绿色到蓝色的可见颜色转换,在含有颜色转换层的ACEL纤维中同样存在类似的现象。这些发现强调了ACEL纤维通过荧光染料集成实现颜色调制和通过频率控制实现动态颜色调谐的双重能力,为可定制的光电应用提供了一条有前景的途径。
图 4 ACEL织物的耐久性能
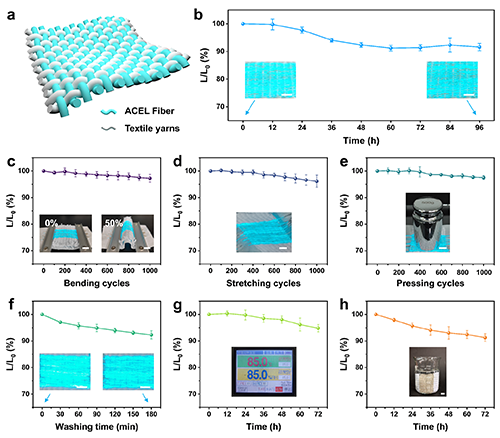
Fig. 4 Performance and durability of ACEL fabrics. (Scale bar, 1 cm. Data presented as mean ± SD, N=3) a Schematic illustration of the plain weave structure of ACEL fabrics. b Durability test results, inset: photographs of ACEL fabric before and after 96 hours of continuous electroluminescence operation. c Bending test, inset: photographs of ACEL fabrics at bending ratios of 0 and 50 %. d Tensile test results, inset: photograph of ACEL fabric under tensile deformation. e Compression test, inset: photograph showing ACEL fabric compressed by a 500 g weight. f Washing test, inset: photograph of ACEL fabric before and after washing for 180 minutes. g Double 85 wet-hot test, inset: interface displaying the parameter settings of the constant temperature and humidity chamber. h Sweat resistance test, inset: photograph of ACEL fabric immersed in synthetic sweat.
为了评估ACEL纤维的可加工性和纺织集成度,使用小型织机织造平纹ACEL织物,织物样品尺寸约3 cm × 5 cm。平纹编织结构保证了纤维均匀分布和在机械变形下保持纤维电致发光的稳定性。制作完成后,进行了一系列的稳定性和耐久性评估,以验证ACEL织物在可穿戴电子纺织品中的实际适用性。大量的耐久性测试证实了ACEL纤维的机械和环境稳定性。具体来说,用ACEL纤维编织的发光织物在连续运行100小时后,其亮度保持了91.6%;1000次弯曲、拉伸和压缩循环测试后,亮度保持率分别为97.2%、96.1%和97.5%;经过多次标准洗涤循环后,纤维的亮度保持了92.3%;经过72小时的双85湿热测试(85°C, 85% RH)后亮度保持了94.8%;经过72小时的耐汗液测试后亮度保持了91.3%。
图 5 ACEL纤维在智能纺织品和交互系统中的应用
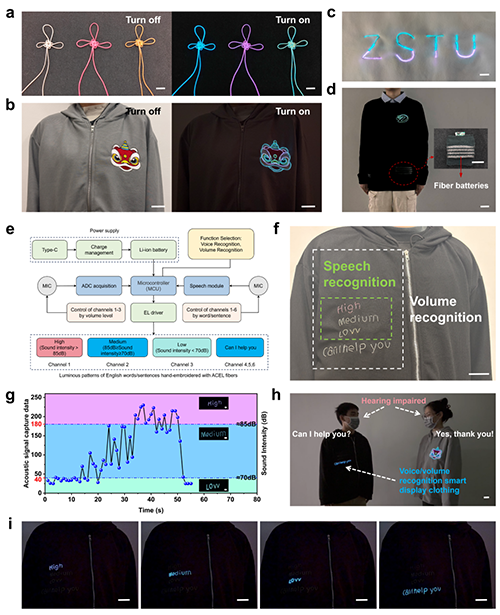
Fig. 5 Applications of ACEL fibers in intelligent textiles and interactive systems. a Auspicious knots are woven using ACEL fibers. Scale bar, 1 cm. b Hand-embroidered outline of the “Lion Dance” pattern, incorporating traditional cultural elements, using ACEL fibers. Scale bar, 5 cm. c Hand-embroidered monogram with color-blocking effects created using ACEL fibers. Scale bar, 1 cm. d Electronic garments incorporating ACEL fiber weaving patterns and embedded fiber batteries. Scale bar, 5 cm. e Block diagram of a sound sensor integrated with an ACEL device for voice recognition and volume detection. f Schematic of the external functional division of an intelligent e-garment with a visual display system for sound sensing. Scale bar, 5 cm. g Hand-embroidered word patterns using ACEL fibers, which alternate illumination based on changes in sound intensity. Scale bar, 1 cm. h Schematic diagram of barrier-free communication for the hearing impaired enabled by a smart electronic garment with a sound-sensing visual display system. Scale bar, 5 cm. i Precise word/sentence illumination controlled by voice recognition in a smart electronic garment equipped with a sound-sensing visual display system. Scale bar, 5 cm.
为了进一步探索ACEL纤维的多功能性和色彩多样性,采用传统编织和手工刺绣技术制作了“吉祥结”、“ZSTU”和“醒狮”等发光显示图案。还将ACEL纤维手工刺绣成校徽图案,并使用课题组前期报道的纤维电池为其供电。将发光和电源模块集成到服装中,展示了ACEL纤维与可穿戴纺织品的无缝集成。此外,将ACEL纤维手工刺绣成基于文本的图案,并与声音传感EL驱动模块集成,构建声音传感显示系统。利用该驱动模块的英语语音识别和声音分贝检测功能,该系统可以有效地将准确识别的声音信号转换为各种应用的视觉反馈。该系统在辅助通信技术方面具有很大的前景,例如为听障人士提供声音可视化显示,以及在特殊工作场所进行环境噪声监测,以提供噪音超标的视觉警报。此外,该系统还可在医院环境中监测特定的声音(例如,咳嗽或喘息),为医疗专业人员提供实时可视化健康预警。
小结:本研究成功地展示了结合共轭静电纺丝和溶液浸涂技术连续制备多色彩ACEL纤维器件的方法。ACEL纤维在保持优异手感的同时显示出明亮、均匀和全向的发光性能。大量的耐久性测试证实了ACEL纤维的机械和环境稳定性。通过将ACEL纤维与具备语音和音量识别的声音传感驱动模块集成在一起,从而扩大了其在听障人士通信、高噪声环境预警和医疗呼吸声监测等领域的潜在应用。
在此,感谢浙江省自然科学基金项目(LY21E030023)和浙江理工大学嵊州创新研究院基金项目(SYY2024C000008)的支持!
通讯作者简介
胡毅,男,博士,教授,博士生导师。浙江理工大学纺织科学与工程学院(国际丝绸学院)副院长,主要从事非水介质染整新技术和柔性电子智能纺织品研究。以第一作者或通讯作者在Advanced Functional Materials, Energy Storage Materials, Advanced Fiber Materials, Nano Letters, Nano Energy,Chemical Engineering Journal等刊物上发表SCI论文70余篇,授权和转化国家发明专利30余项。获得国家级教学成果二等奖和浙江省教学成果特等奖各1项;主持获得中国纺织工业联合会教学成果一、二、三等奖,浙江省自然科学奖三等奖和中国商业联合会科技进步奖二等奖各1项。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-025-00579-w
