与许多生物组织一样,皮肤可以自我保护和修复,通过愈合伤口恢复其机械和电气特性,同时具有应变硬化特性,即在大变形下,皮肤的强度和韧性显著增加,以避免严重的外部刺激而造成伤害,因此,开发具有应变硬化特性的多功能模拟皮肤水凝胶至关重要。传统的制备应变硬化水凝胶的方法包括将纳米离子共混到聚合物中或者合成嵌段结晶共聚物,但很难调节材料的多功能性,比如自愈合、自黏附、离子导电等。近年来,通过对聚乙烯醇解冻-冷冻或者化学交联形成凝胶,实现原位结晶,从而赋予水凝胶应变硬化的性能,但是,这些方法比较耗时,很难在应用于3D打印或者临床医学中。
与聚乙烯醇相比,聚乙烯胺(PVAm)具有相似的结构,主链含有丰富的氨基,具有更高的反应活性。PVAm被广泛应用于造纸等行业,但却很少用于构建应变硬化水凝胶。近期,江南大学张丹教授团队提出了一种通过PVAm凝聚诱导结晶实现多功能性水凝胶,所制备的水凝胶整合了可拉伸性(约1300%伸长率)、韧性(227 kPa)、应变硬化性(增加约10倍)、自粘着力(90 J m-2)、自愈合性(约80%韧性愈合效率)和离子电导率(0.22 mS m-1)。这也是首次通过化学交联方法构建具有上述综合性能的水凝胶,这种方便的策略将为设计多功能皮肤模拟材料开辟新的视野。
与已发表的通过不同反应物之间的非共价相互作用实现凝聚来制备具有不同性能的水凝胶不同,在该团队设计的系统中,PVAm聚合物之间发生凝聚。通过在PVAm溶液中加入不相溶的交联剂实现相分离,形成PVAm聚集相和PVAm松散相,在液-液边界发生PVAm和乙二醇二缩水甘油醚(EGDE)的化学反应,将PVAm链段受限在小的有限的体积内,PVAm聚合相中的高浓度导致较小的临界晶核和较高的成核率,同时PVAm之间的相互作用(如氢键)有利于自外延生长成核促进晶体在密相中结晶。此外,在该体系中引入Zn(NO3)2,可产生PVAm和Zn2+金属-配体配位,提供自黏附、自愈合和离子导电性(Figure 1)。
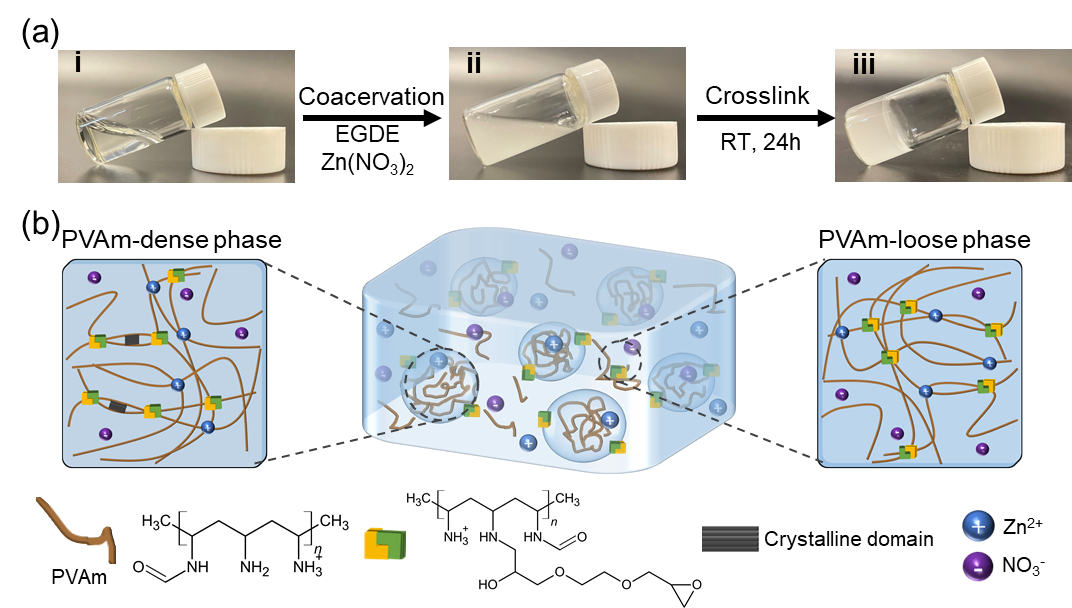
Figure 1. (a) Images of the preparation process of PVAm hydrogel. (b) Schematic illustration of the PVAm hydrogel which is composed of PVAm-dense and PVAm-loose phase. The crystalline domain formed in the PVAm-dense phase provides strain-stiffening property, while the amorphous domain is responsible for the self-healing, adhesion, and ionic conductivity characteristics.
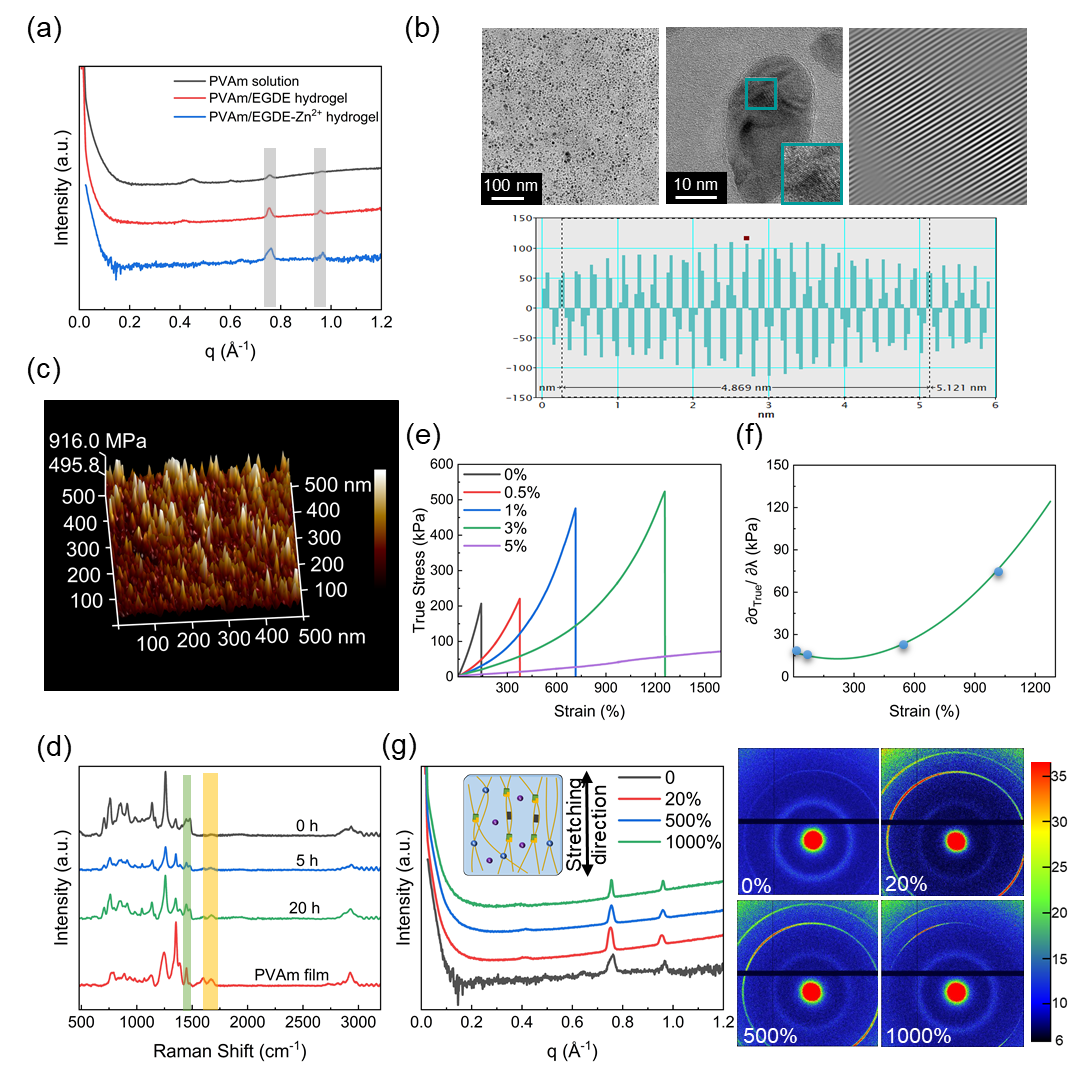
为证明该猜想,使用小角X射线散射(SAXS),广角X射线散射(WAXS),TEM,AFM和Raman对PVAm水凝胶进行表征(Fig. 2a-d)。和PVAm溶液相比,PVAm/EGDE水凝胶在0.75和0.96 ?-1处的峰强增大,表明形成了结晶区。Zn2+的加入并未对水凝胶的结晶有任何影响,说明Zn2+主要作用在水凝胶的非晶区,即PVAm松散相中。除此之外,X射线衍射数据显示,物理交联和在均相中发生化学反应生成的PVAm凝胶均未发现峰,由此可以说明在凝聚作用下的化学交联对结晶是必要的。
除了应变硬化,自黏附、自愈合、弹性和离子导电性也是离子皮肤所需具备的性能。通过压痕、剪切拉伸和180度剥离试验评估黏附性能(Fig. 3a),数据表明,黏附力随着Zn2+浓度的增加而提高(Fig. 3b-d),但当Zn2+浓度达到5%时出现内聚破坏,当浓度低于5%时,水凝胶均可轻松得从猪皮上剥离,因此选择含有3%Zn2+的水凝胶用于后续研究。除猪皮外,该水凝胶可以与其他基材紧密黏附,包括玻璃、聚四氟乙烯、铜和棉织物。通过在增加应变(100%-1000%)和固定应变(1000%)下进行循环拉伸和缺口拉伸试验可以发现水凝胶具有很高的弹性和低滞后(Fig. 3e-g)。此外,该PVAm/0.5EGDE-3%Zn2+水凝胶具有很好的自愈合性,在室温下恢复1小时后仍可拉伸原长的11倍左右,具有约80%的愈合效率(Fig. 3h-i)。

Figure 3. Adhesive, elasticity, and self-healing properties of the PVAm hydrogels. (a) Schematics of the indentation, lap shear, and 180 degree peeling tests. (b) Indentation, (c) lap shear, and (d) peeling curves of PVAm/0.5EGDE-Zn2+ hydrogels with different concentrations of Zn(NO3)2 (0%, 0.5%, 1%, 3%, and 5%). (e) Successive tensile loading–unloading curves of PVAm/0.5EGDE-3%Zn2+ hydrogel as stretched to different strains. (f) Cyclic tensile curves of PVAm/0.5EGDE-3%Zn2+ hydrogel at a fixed maximum strain of 1000% for uninterrupted 10 cycles. (g) Tensile stress-strain curves of original and notched PVAm/0.5EGDE-3%Zn2+ hydrogel. (h) Two PVAm/0.5EGDE-3%Zn2+ hydrogel segments healed together for 1 h at room temperature to withstand stretching. The hydrogels were colored blue with methylene blue. (i) Tensile stress-strain curves of original and self-healed hydrogels.

相关研究成果以“Coacervation-Based Method for Constructing a Multifunctional Strain-Stiffening Crystalline Polyvinylamine Hydrogel”为题发表在《ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces》上,该文章的第一作者为吴赟博士,目前为江南大学纺织科学与工程学院助理研究员,通讯作者为江南大学张丹教授/司鹏翔副教授。
原文链接:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.2c08838
- 福州大学邹志刚院士团队吕晓林 Macromolecules:基于强、弱离子相互作用的应变硬化聚离子液体弹性体 2024-03-28
- 江南大学陈明清/施冬健课题组 ACS AMI:类皮肤组织应变硬化能力的图案化水凝胶用于应变传感器 2023-10-15
- 华南理工大学孙桃林教授团队《Macromolecules》:拓扑结构可调的梳状聚合物粘合剂 2023-02-18
- 浙江大学李伯耿、刘平伟团队 Macromolecules:动态交联构建结晶侧链和弹性骨架的高性能聚烯烃热塑性弹性体 2024-02-16
- 烟台大学刘洪亮教授团队 AFM:具有优异机械性能、灵活可加工的高性能离子凝胶 2023-05-07
- 西安交大唐敬达与哈佛大学Joost J. Vlassak教授 JMPS:动态化学交联水凝胶的光可控断裂 2022-10-26
- 北海道大学龚剑萍/深圳大学范海龙 Macromolecules:基于凝聚层自发相变的水/油下强黏附凝胶 2025-10-03
