The research work on "Efficient Synergistic Chemotherapy through Self-Delivery Nanomicelles of Platinum-Containing Supramolecular Drugs" has been published online in Biomacromolecules
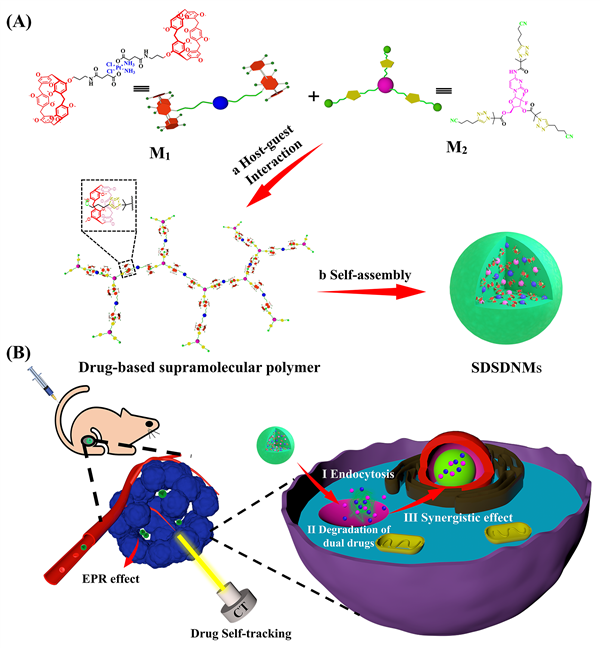
Supramolecular self-delivery systems for drugs offer distinct advantages over traditional self-delivery systems, as they harness the unique characteristics of supramolecular interactions, such as dynamic reversibility and stimulus responsiveness. These systems have the potential to achieve effective drug delivery within the body. However, a significant challenge arises from the lack of real-time feedback on the evolution process of drugs within tumor tissues. This limitation hampers accurate determination of the optimal dosage and administration time for supramolecular self-delivery systems, resulting in suboptimal anti-tumor therapeutic effects. Recently, our research group reported a self-tracking supramolecular drug self-delivery nanomicelle. This nanomicelle can achieve CT imaging in mice, enabling precise tracking of its distribution in tumor tissues and real-time feedback on the evolution of the drug. This information allows for determining the optimal dosage and administration time, ultimately leading to efficient synergistic chemotherapy. This self-tracking supramolecular drug self-delivery system with tracing functionality provides a new option for effective synergistic chemotherapy.
The research findings have been published online in "Biomacromolecules"
(Journal link: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.1c00173).
The co-first authors of the paper are doctoral students Chengfei Liu and Muqiong Li from the research group, while Associate Professor Li Fan and Professor Wei Tian from the Air Force Medical University are the corresponding authors of the paper.