Copolymerization of ethylene with norbornenecatalyzed by cationic rare earth metal fluorenylfunctionalized N-heterocyclic carbene complexes
writer:Baoli Wang, Tao Tang, Yuesheng Lia and Dongmei Cui
keywords:rare earth metal ;complexes; ethylene ; norbornene; feed ratio
source:期刊
specific source:http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlepdf/2009/dt/b910306f
Issue time:2009年
Rare
earth metal bis(alkyl) complexes attached
by fluorenyl modified N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC)
(Flu-NHC)Ln(CH2SiMe3)2 (Flu-NHC = (C13H8CH2CH2(NCHCCHN)C6H2Me3-2,4,6);
Ln = Sc (2a); Y (2b); Ho (2c); Lu (2d)),
(tBuFlu-NHC)Ln(CH2SiMe3)2 (tBuFlu-NHC
= 2,7-tBu2C13H6CH2CH2(NCHCCHN)C6H2Me3-2,4,6;
Ln = Sc (1a); Lu (1d)) and attached
byindenyl modified N-heterocyclic carbene (Ind-NHC)Ln(CH2SiMe3)2 (Ind-NHC
= C9H6CH2CH2(NCHCCHN)C6H2Me3-2,4,6;
Ln = Sc (3a); Lu (3d)), under
the activation of AliBu3 and [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4],
showed varied catalytic activities toward homo-
andcopolymerization of ethylene and norbornene. Among which
the scandium complexes, in spite of ligand type, exhibited medium to
high catalytic activity for ethylenepolymerization (105 g molSc?1 h?1 atm?1),
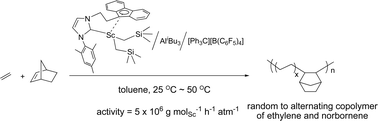
but all were almost inert to norbornenepolymerization. Remarkably, higher
activity was found for
the copolymerization ofethylene and norbornene when
using Sc based catalytic systems, which reached up to 5 ×
106 g molSc?1 h?1 atm?1 with 2a.
The composition of the isolated copolymer was varying from random to
alternating according to the feed ratio of the two monomers (rE =
4.1,rNB = 0.013). The molecular structure of
complex 1d was characterized by X-ray analysis. The
influences of structural factors of complexes
and polymerization conditions on both the catalytic
activity and the norbornene content in
the copolymer were discussed.