- Hydrogel microneedles with multifunctional strategy for prolonged hyperuricemia management
- 来源:江国华教授个人网站 2025-03-26
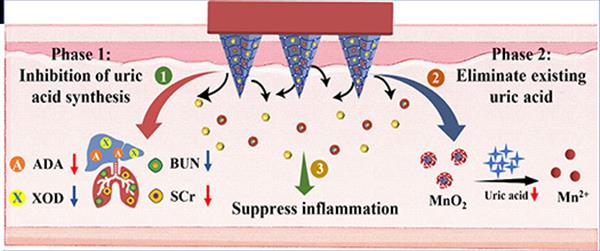
Abstract: An efficient and long-term stable non-oral drug delivery system is preferable for treating hyperuricemia, as it can minimize adverse effects and prolong treatment efficacy. Herein, the hydrogel microneedles (HMNs) system with dual modulation strategy was proposed to regulate the serum uric acid (SUA) levels. First, allopurinol (AP) loaded metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) (ZIF-8) composite nanoparticles were absorbed on to the lamella of MnO2 nanosheets to form the environment-responsive nanoformulations (AP@ZIF-8@MnO2, APZM). Then, these environment-responsive nanozymes and free AP were further mixed with the methacrylate hyaluronic acid (MeHA) to fabricate HMNs by vacuum template and UV light cross-linking technologies. In vitro experiments on mice models showed that the free AP could be rapidly released to inhibit the production of UA after the these MNs absorption of interstitial fluid. And APZM nanoformulations encapsulated in HMNs could be slowly released due to the swelling of HMNs. The MnO2 from APZM could be acted as a potent oxidase-like nanoenzyme, scavenging the existing SUA. And the degradation of ZIF-8 triggered the high SUA levels micro-environment provided a secondary release of AP to maintain the longer normouricemia state. The SUA level could be maintained for more than 32 h under the normal level, leading a long-term therapeutic effect.
Keywords: Microneedles, hyperuricemia, serum uric acid (SUA) levels, ZIF-8, MnO2
- [来源:中国聚合物网]
- 了解更多请进入: 江国华教授个人网站
- · κ-Carrageenan and hyaluronic acid composite injectable hydrogel-containing isosorbide mononitrate-loaded liposomes for treatment of myocardial?infarction
- · Review on engineered polymer microneedles for drug delivery and disease diagnosis
- · Platelet membrane-camouflaged bioactive glass nano-formulations for enhanced drug delivery in the treatment of acute arterial thrombosis
- · Iontophoresis-driven transdermal drug delivery system based on porous microneedles for hyperuricemia treatment.