- A three-dimensional printable conductive composite dressing for accelerating wound healing under electrical stimulation
- 来源:江国华教授个人网站 2024-10-16
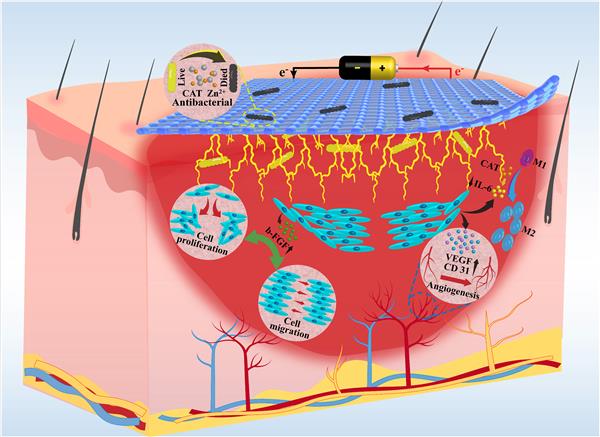
Abstract: In this study, a bioink based on poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) and k-carrageenan network was prepared using conductive polymer (PEDOT:PSS) as conducting medium, and (+)-Catechin-loaded mesoporous ZnO (CmZnO) as antibacterial and anti-inflammatory active medium. 3D conductive composite dressing was further fabricated by an extrusion 3D printing technology. Our results showed that the as-obtained composite dressing had suitable conductivity, efficient blood clotting capacity, and good adhesiveness. It also showed that the as-fabricated conductive composite had 92.9% and 95.6% antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Escherichia coli (E. coli), respectively. Furthermore, the conductive dressing with an optimal electrical stimulation (ES) parameter showed in vivo blood clotting capacity, and it enhanced in vivo wound healing process in a full-thickness skin defect model than commercial dressings by upregulating the gene expression of growth factors including CD-31 and downregulating inflammatory factor expression of IL-6.
Keywords: conductive dressings, 3D printing, electrical stimulation, wound healing
- [来源:中国聚合物网]
- 了解更多请进入: 江国华教授个人网站
- · In-situ blood glucose level detection based on a non-enzymatic microneedle biosensor
- · Hyaluronic Acid and Polyacrylamide Composite Hydrogel Containing Viscid Germander Herb for Wound Closure and Healing
- · Highly adhesive, stretch, antioxidative and antibacterial double-network hydrogel containing artemisinin for?infected wound?closure and healing
- · Porous microneedle-mediated continuous glucose monitoring based on reverse iontophoresis