Enhanced Gene Transfection Efficiency of PDMAEMA by Incorporating Hydrophobic Hyperbranched Polymer Cores: Effect of Degree of Branching
writer:Yu, S. R.; Chen, J. X.; Dong, R. J.; Su, Y.; Ji, B.*; Zhou, Y. F.*; Zhu, X. Y.*; Yan, D. Y.
keywords:gene transfection , PDMAEMA, Hyperbranched Polymer
source:期刊
specific source:Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 3324. http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2012/py/c2py20487h#
Issue time:2013年
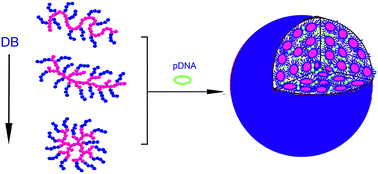
Poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl
methacrylate) (PDMAEMA) is a well-known cationic polymer candidate for non-viral
vectors for gene transfection. However, such an application has been greatly
limited due to the cytotoxicity of the polymers. Herein, PDMAEMAs are grafted
from hydrophobic hyperbranched PEHO cores (PEHO means
poly(3-ethyl-3-(hydroxymethyl)-oxetane)), and the obtained hyperbranched
multiarm copolymers of PEHO-g-PDMAEMAs show higher transfection
efficiency than that of branched polyethylenimine (PEI) and PDMAEMA
homopolymers, due to the improved cytotoxicity, DNA compaction, buffering
ability and cellular uptake. In addition, to disclose the structure–property
relationship, a series of PEHO-g-PDMAEMAs with different topological
architectures are synthesized by changing the degrees of branching (DBs) of the
PEHO cores and the lengths of the PDMAEMA arms. The ability of these vectors in
DNA compaction, buffering ability, cytotoxicity and gene transfection efficiency
is also investigated. It has been found the gene transfection efficiency of the
vectors is dependent on the DB of the PEHO cores, but almost independent of the
PDMAEMA arms in the experimental range.