Effect of Surface Acetylation of Chitin Nanocrystals on the Preparation and Viscoelasticity of Sunflower Seed Oil-in-Water Pickering Emulsions
writer:Sumin Yu, Guangni Peng, Defeng Wu*
keywords:chitin nanocrystals; Pickering emulsions; emulsion viscoelasticity.
source:期刊
specific source:International Journal of Biological Macromolecules
Issue time:2024年
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 254, 127883.
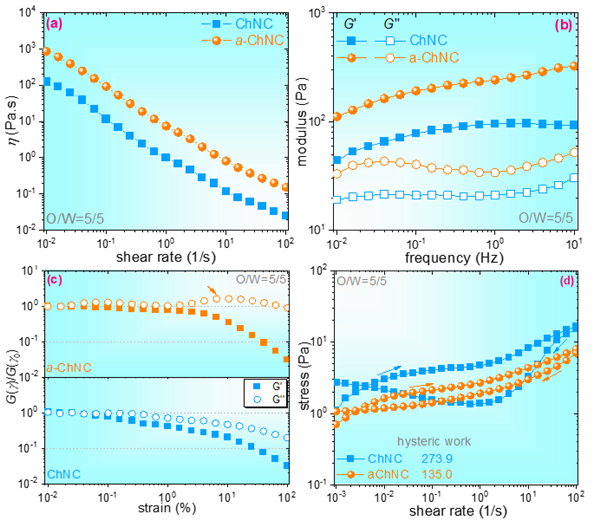
Acetylated chitin nanocrystals (ChNCs) were used as stabilizer in this work to prepare sunflower seed oil-in-water emulsions for the morphological and rheological studies. The results revealed that the acetylation with moderate degree of substitution (0.38) reduced hydrophilicity and increased surface charge level of rod-like ChNCs, and as a result, significantly improved the emulsifying ability of ChNCs. At the same oil/water ratio and particle loading, the emulsions stabilized with the acetylated ChNCs had far smaller droplet size (~3 μm) as compared to the emulsions stabilized with the pristine ChNCs (5~7μm). The increased droplets numbers and improved surface coating level resulted in the enhanced viscous resistance and yield stress level, which improved the physical stability of the acetylated ChNC-stabilized emulsions as a result. In addition, the droplet clusters easily formed in this system, contributing to weak strain overshoot and decreased large-deformation sensitivity during dynamic shear flow. Therefore, the acetylated ChNC-stabilized system showed enhanced transient stress overshoot during startup flow and weakened thixotropy during cyclic ramp shear flow as compared to the pristine ChNC-stabilized system. The relationships between surface acetylation of ChNCs and flow behavior of emulsions were then established, which provide valuable information on the modulation of the ChNC-stabilized Pickering emulsions.
PDF DOWNLOAD:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0141813023047827