研究背景
在碳基材料中,拓扑缺陷是不可避免的存在,但这些缺陷的固有电催化活性和机制尚未完全探索。绿色氢作为环保的零碳能源,在未来氢能系统中起着关键作用,主要通过使用可再生能源(如太阳能和风能)进行水电解来生产。然而,目前绿色氢的经济可行性低于灰氢等其他类型,且贵金属催化剂(如Pt/C、IrO?、RuO?)在水电解中仍不可或缺。特别是,对于氢析出反应(HER),昂贵的Pt仍然占据催化性能的顶峰。因此,研究如何使用更便宜的贵金属(如Ru)并探索其催化机制,对于降低水电解成本具有重要意义。
工作内容
通过密度泛函理论(DFT)计算,预测了富含五边形环的碳(PRC)结构中五边形环的电化学反应性。发现五边形拓扑缺陷能够优化碳基体的电子性质,如降低带隙能量、优化p带中心和提高电子再分布程度,从而调节关键中间体的吸附。通过碱刻蚀技术处理富勒烯材料(C60),形成富含五边形环的碳纳米材料(PRC)。使用湿化学法和热还原法将Ru物种锚定在PRC上,形成Ru@PRC催化剂。利用光谱学和电子显微镜技术,揭示Ru@PRC中五边形缺陷的关键作用,以及C原子和Ru原子之间的p-d轨道杂化效应。研究表明,C-p轨道和Ru-d轨道之间的强杂化调节了Ru@PRC结构的电子状态,增强了其HER活性。测试了Ru@PRC催化剂在不同pH介质中的HER活性,特别是在碱性条件下表现出优异的性能。Ru@PRC在电流密度为10 mA cm?2时,过电位仅为28 mV,远低于Pt/C催化剂。
工作创新点
1.揭示了五边形缺陷对HER的积极作用:首次通过实验和理论相结合的方法,证明了五边形缺陷可以作为HER的活性位点,显著提高碳基材料的HER活性。
2.p-d轨道杂化效应:提出了C原子(五边形环中)和Ru原子之间的p-d轨道杂化效应,这种效应促进了电子从Ru簇向五边形环的快速转移,减弱了Ru与氢中间体的结合强度,从而增强了HER活性。
3.高效催化剂的制备:成功制备了Ru@PRC催化剂,该催化剂在HER中表现出优异的催化活性和稳定性,特别是在碱性条件下,其性能显著优于商业Pt/C催化剂。
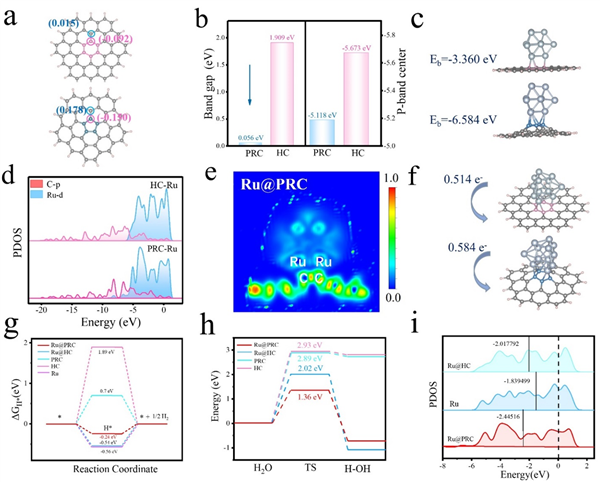
Figure 1. (a) Charge densities of PRC and HC. (b) Band gap and calculated p-band center of PRC and HC. (c) Geometric optimization results and binding energies of Ru@HC and Ru@PRC. (d) PDOS of C, Ru for Ru@PRC and Ru@HC. (e) ELF analyses of Ru@PRC. (f) Bader charge transfer on Ru@HC and Ru@PRC models. (g) HER Gibbs free energy diagrams of Ru@PRC, Ru@HC, PRC, HC and Ru models. (h) Water-dissociation pathways of Ru@PRC, Ru@HC, PRC, HC models. (i) d-band center analyses of Ru@HC, Ru and Ru@PRC.

Figure 2. (a) Schematic of the synthesis process for Ru@PRC. (b) TEM images of PRC. (c) Ac-STEM image of PRC. (d) Filtered image of PRC. (e) TEM image of Ru@PRC. (f) Ac-STEM image Ru@PRC. (g) Filtered image of Ru@PRC. (h-k) Elemental mapping of Ru@PRC.
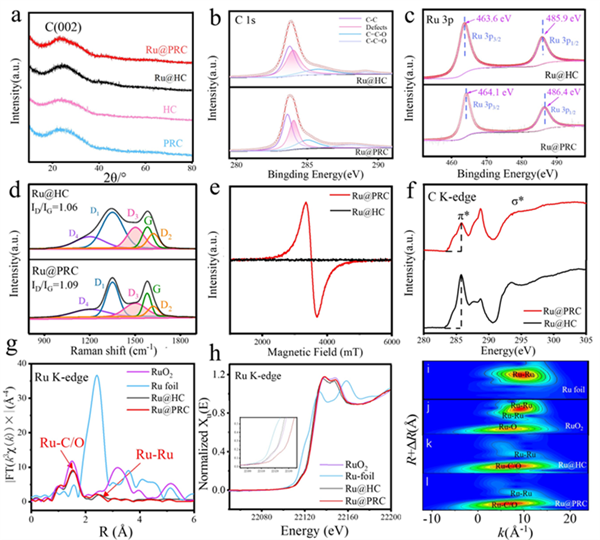
Figure 3. (a) XRD patterns of Ru@PRC, Ru@HC, PRC and HC. (b) C 1s and (c) Ru 3p fitting results of Ru@HC and Ru@PRC. (d) Raman spectra and (e) EPR results of Ru@HC and Ru@PRC. (f) C K-edge NEXAFS spectra of Ru@PRC and Ru@HC. (g) EXAFS and (h) XANES spectra and (i-l) wavelet transform (WT-) analyses of RuO2, Ru foil, Ru@HC and Ru@PRC.
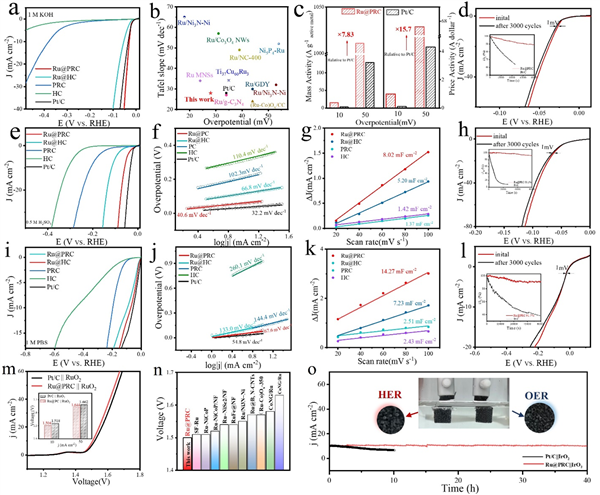
Figure 4. (a) Polarization curves (with iR-correction) of Ru@PRC, Ru@HC, PRC, HC and Pt/C catalysts in 1 M KOH solution. (b) Comparison of catalytic performance of Ru@PRC with other reported alkaline HER catalysts. (c) Mass activity and price activity at the overpotentials of 10 and 50 mV for Ru@PRC and Pt/C catalysts. (d) Stability test of Ru@PRC in alkaline media. (e) Polarization curves (with iR-correction) of Ru@PRC, Ru@HC, PRC, HC and Pt/C catalysts in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution. (f) Relevant Tafel slopes. (g) Cdl calculation of Ru@PRC, Ru@HC, PRC, HC, and Pt/C in acidic media. (h) Stability test of Ru@PRC in acidic media. (i) Polarization curves (with iR-correction) of Ru@PRC, Ru@HC, PRC, HC and Pt/C catalysts in 1 M PBS solution. (j) Relevant Tafel slopes. (k) Cdl calculation of Ru@PRC, Ru@HC, PRC, HC and Pt/C in neutral media. (l) Stability test of Ru@PRC in neutral media. (m) Polarization curves of overall water splitting performance of Ru@PRC || RuO2 couple and Pt/C || RuO2 couple in alkaline media. (n) Comparison of overall water splitting performance of Ru@PRC with other reported alkaline HER catalysts. (o) durability test of Ru@PRC || IrO2 and commercial Pt/C|| IrO2.
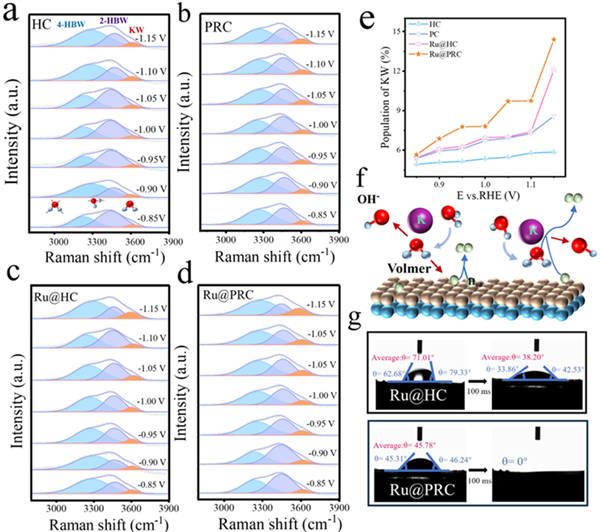
Figure 5. In situ Raman spectra of interfacial water on (a)HC, (b) PRC, (c) Ru@HC and (d) Ru@PRC in 1M KOH solutions (E versus RHE). (e) The population of KW from in situ Raman spectra. (f) Schematic showing interfacial water dissociation on Ru@PRC. (g) Contact angles of Ru@HC and Ru@PRC using the KOH electrolyte.
原文信息
Lei Gong, Fanjie Xia, Jiawei Zhu, Xueqin Mu, Ding Chen, Hongyu Zhao, Lei Chen, Shichun Mu, Hydrogen Evolution Reactivity of Pentagonal Carbon Rings and p-d Orbital Hybridization Effect with Ru, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, e202411125.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202411125