作者:Tangxin Zhang,Hao Zhang,Tiantian Zhu,Yuhua Mao,Jiayuan Wang,Lingyu Zhu,Jianli Wang
关键字:Dissolved oxygen,Catalytic membrane,Palladium nanoparticles,Hybrid microgel
论文来源:期刊
具体来源:Chemical Engineering Journal
发表时间:2025年
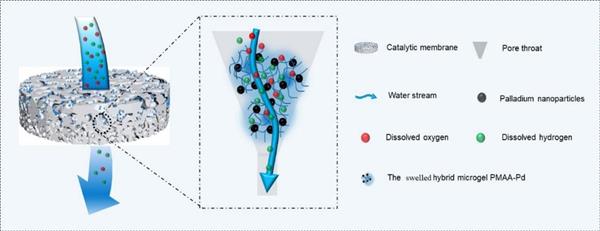
在脱氧水制备领域,开发兼具高效性与低污染特性的催化剂仍面临重大挑战。本研究创新性地构建了一种新型复合催化膜,其通过亲水性聚合物网络实现钯纳米颗粒的高度分散与流体充分接触暴露。基于动态过滤-可逆固定策略构筑的催化膜在制备与应用中展现出卓越的柔性特征。为此,本研究设计并搭建了柔性连续化水处理装置用于评估催化膜除氧性能。实验表明:在常温条件下,当水停留时间为32.3秒时,三层复合催化膜可将水中溶解氧浓度降至10 ppb。这种独特构型的催化膜可满足实验室装置与仪器预处理等场景的便携式与柔性除氧需求。
In de-oxygen water preparation, it is still a challenge to develop a highly efficient catalyst with less pollution on produced water. Herein, we invented a novel catalytic membrane, in which palladium nanoparticles were well dispersed and exposed sufficiently to the fluid with the help of hydrophilic polymer networks. These catalytic membranes created by dynamic filtration and reversible fixation offer exceptional flexibility in preparation and application. An apparatus for flexible and continuous chemical removal of dissolved oxygen from water was built up and applied to determine the performance of catalytic membranes. When the residence time was 32.3 s, the concentration of DO could be reduced to 10 ppb by a tri-layer catalytic membrane at ambient temperature. This uniquely configured catalytic membrane could be applied in portable and flexible DO requirements, such as experimental setups and pretreatment of instruments.
国家自然科学基金(资助号:22178317、22109138)资助。