Synthesis and Characterization of novel biodegradable block copolymer poly(ehylene glycol)-block-poly(L-lactide-co-2-mthyl-2- carboxyl-propylene carbonate).
作者:Huili Guan, Zhigang Xie, Peibiao Zhang, Xin Wang, Xuesi Chen, Xianhong Wang and Xiabin Jing
关键字:biodegradable; carbonate; functionalization of polymers; polylactide;
论文来源:期刊
具体来源:Journal of Polymer Science: Part A:Polymer Chemistry, 2005, 43:4771-4780
发表时间:2005年
[Abstract]: An amphiphilic block copolymer, poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(L-lactideco-
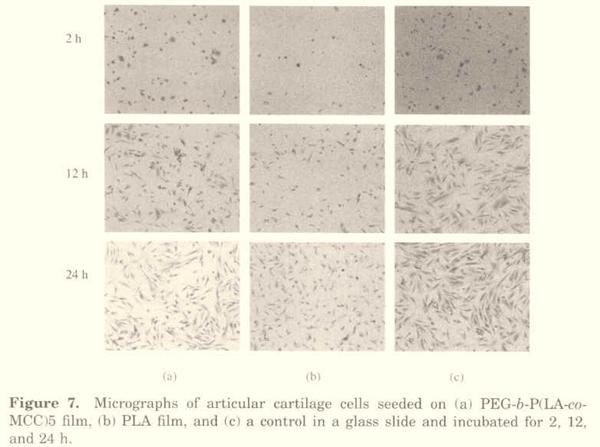
2-methyl-2-benzoxycarbonyl-propylene carbonate) [PEG-b-P(LA-co-MBC)], was synthesized in bulk by the ring-opening polymerization of L-lactide with 2-methyl-2-benzoxycarbonyl-propylene carbonate (MBC) in the presence of poly(ethylene glycol) as a macroinitiator with diethyl zinc as a catalyst. The subsequent catalytic hydrogenation of PEG-b-P(LA-co-MBC) with palladium hydroxide on activated charcoal (20%) as a catalyst was carried out to obtain the corresponding linear copolymer poly(ethyleneglycol)-blockpoly(L-lactide-co-2-methyl-2-carboxyl-propylenecarbonate) [PEG-b-P(LA-co-MCC)] with pendant carboxyl groups. DSC analysis indicated that the glass-transition temperature (Tg) of PEG-b-P(LA-co-MBC) decreased with increasing MBC content in the copolymer, and Tg of PEG-b-P(LA-co-MCC) was higher than that of the corresponding PEG-b-P(LAco-MBC). The in vitro degradation rate of PEG-b-P(LA-co-MCC) in the presence of proteinase K was faster than that of PEG-b-P(LA-co-MBC), and the cytotoxicity of PEG-b-P(LA-co-MCC) to chondrocytes from human fetal arthrosis was lower than that of poly(L-lactide).