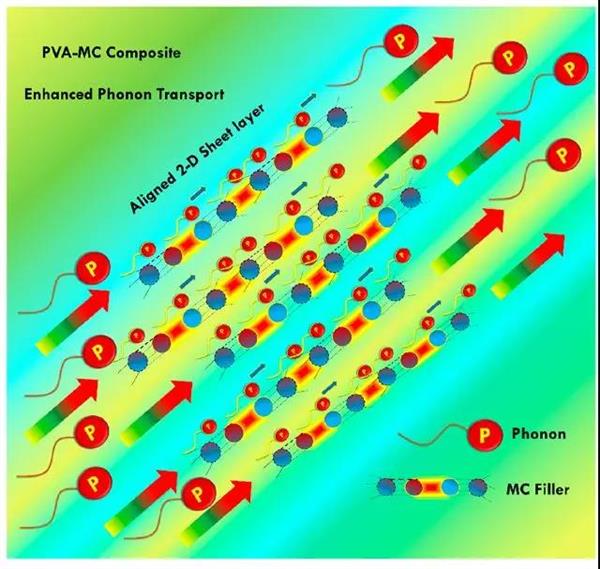
Abstract: Polymer composites are of great interest in thermal conduction applications, while poor filler dispersion and enormous phonon scattering at composite interface become the critical bottleneck for efficient thermal conduction. This work presents a multiple hydrogen bonded supramolecular crystal, melamine-cyanurate (MC), with remarkable potential to develop self-assembled 2-D layered sheet structures while at the same time strengthening thermal interfaces. Such a composite is prepared by an in situ coprecipitation method resulting in homogeneous distribution of MC crystals. An extensive network of multiple hydrogen bonds present in this supramolecular assembly along with aligned layered structure facilitated efficient phonon transport. As a result, 65% enhancement of TC can be achieved by incorporating 2D MC crystals in the composites. The mechanism of MC crystal assembling and orientation in the composite are discussed as well. Overall this work offers a new strategy for the design and development of thermally conductive materials via supramolecular assembling.