102. Preparation of chitosan-based multifunctional nanocarriers overcoming multiple barriers for oral delivery of insulin
作者:Lei Li, Guohua Jiang,* Weijiang Yu, et al.
关键字:nanocarriers; chitosan; insulin; oral delivery; hypoglycemic effect
论文来源:期刊
具体来源:Materials Science and Engineering C, 2017, 70, 278-286
发表时间:2017年
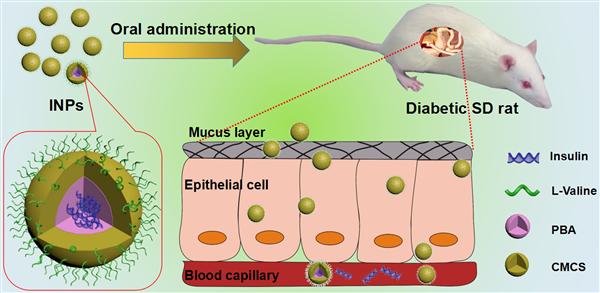
To overcome multiple barriers for oral delivery of insulin, the chitosan-based multifunctional nanocarriers modified by L-valine (LV, used as a target ligand to facilitate the absorption of the small intestine) and phenylboronic acid (PBA, used as a glucose-responsive unit) have been designed and evaluated in this study. The resultant nanocarriers exhibited low cytotoxicity against HT-29 cells and excellent stability against protein solution. The insulin release behaviors were evaluated triggered by pH and glucose in vitro. The chemical stability of loaded insulin against digestive enzyme were established in presence of simulated gastric fluid (SGF) containing pepsin and simulated intestinal fluid (SIF) containing pancreatin, respectively. The uptake behavior of HT-29 cells was evaluated by confocal laser scanning microscope. After oral administration to the diabetic rats, an effective hypoglycemic effect was obtained compared with subcutaneous injection of insulin. This work suggests that chitosan-based multifunctional nanocarriers may be a promising drug delivery carrier for oral administration of insulin.