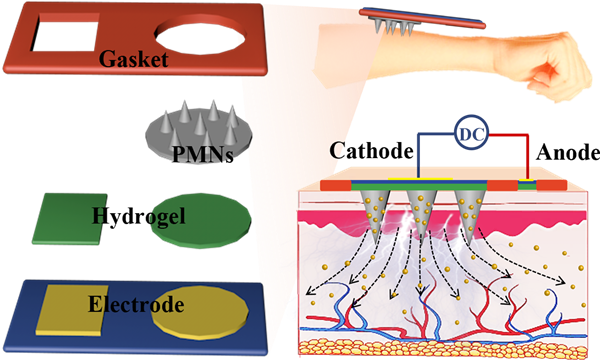
Iontophoresis-driven transdermal drug delivery system based on porous microneedles for hyperuricemia treatment.
作者:Rui Wang, Han Wang, Rui Yao, Yan Li, Sedrati Manar, Lei Nie, Khaydar E. Yunusov, Jianwei Pan, Guohua Jiang*
关键字:Porous microneedles, iontophoresis-driven, hyperuricemia.
论文来源:期刊
具体来源:International Journal of Pharmaceutics
发表时间:2025年
Abstract: An iontophoresis-driven porous microneedles (IPMNs) system has been developed for hyperuricemia management, which can be effectively prolong the anti-hyperuricemia effect. Porous microneedles (PMNs) with good biocompatibility, high porous volume, and excellent substance exchange capacity were firstly prepared for drug transdermal delivery and active iontophoresis. In vitro experiments showed that the transdermal delivery efficiency of anti-hyperuricemia drug (Allopurinol, AP) could be controlled using the iontophoresis current of IPMNs system. The drug delivery efficiency could be enhanced by 6.34-folds with iontophoresis under constant voltage of 1.5 V for 30 min. In vivo transdermal delivery of AP on mice models using IPMNs system exhibited an effective anti-hyperuricemia response. The serum uric acid (SUA) level could be dropped to ~158.2 μmol/L within 2 h, and maintaining for 7 h under the normal level, leading a long-term therapeutic effect. This IPMNs system exhibits a low cost, user-friendly, and active delivery, showing great potential for hyperuricemia self-administration.
Keywords: Porous microneedles, iontophoresis-driven, hyperuricemia.