Microneedles fabricated from alginate and maltose for transdermal delivery of insulin
作者:Yang Zhang, Guohua Jiang, * Weijiang Yu, Depeng Liu, Bin Xu
关键字:Microneedles; Transdermal delivery; Hypoglycemic effect; Diabetes
论文来源:期刊
具体来源:Materials Science and Engineering, C
发表时间:2018年
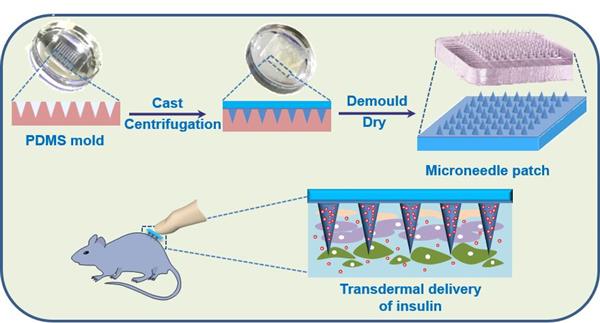
To reduce the inconvenient and painful of subcutaneous needle injection, the calcium ion cross-linked alginate/maltose (Ca2+/Alg-Mal) composite microneedles have been fabricated by a template method. The as-prepared microneedles exhibited a strong mechanical properties with the highest failure force around 0.41 N/needle. The biological activity and stability of loaded insulin in microneedles were investigated. Due to the good mechanical properties and excellent biocompatibility, the as-prepared microneedles have been applied for transdermal delivery of insulin on diabetic Sprague-Dawley (SD) rat models in vivo. After transdermal administration to the diabetic rats, the released insulin from biodegradable composite microneedles exhibit an obvious and effective hypoglycemic effect with relative pharmacological availability (RPA) and relative bioavailability (RBA) at 94.1±5.6% and 93.7±4.7% compared with that of subcutaneous injection route. This work suggests that as-prepared Ca2+/Alg-Mal microneedles can be used to encapsulate insulin and have a potential application in diabetes treatment via transdermal ingestion.