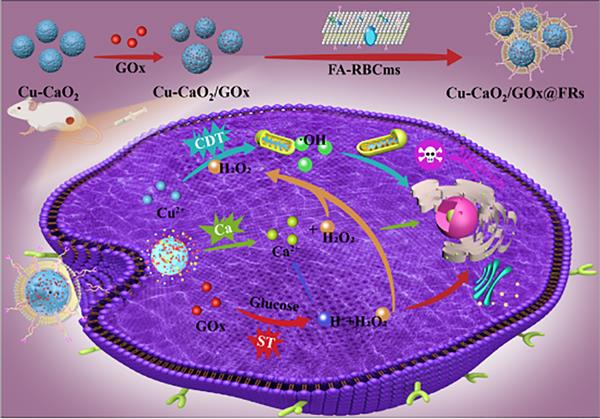
由硕士研究生张骏豪等完成的研究论文“A red cell membrane-camouflaged nanoreactor for enhanced starvation/chemodynamic/ion interference therapy for breast cancer”在Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces发表!
Abstract: In this study, a multifunctional Cu-doped CaO2 nanoreactor loaded with GOx and camouflaged with a folic acid�modified cell membrane was developed for breast cancer treatment. The as-developed composite nanoreactor showed a synergistic effect on calcium overload to damage mitochondria, thus killing tumor cells to achieve ion interference therapy (IIT). The loaded GOx could deplete glucose to “starve” tumor cells. The H2O2 released by
CaO2 decomposition and enzyme catalytic reactions from GOx could not only be highly toxic in the tumor microenvironment but also enhance the efficiency of chemodynamic therapy (CDT) with Cu2+. The red blood cell membranes modified by folic acid achieved a combination of active targeting and passive targeting, thereby enhancing the targeting ability of the as-prepared multifunctional composite nanoreactor and prolonging its retention time at the tumor sites for more than 48 h.