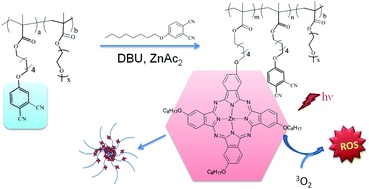
[Polym Chem] A novel approach to synthesize polymers for potential photodynamic therapy: from benzenedinitrile to phthalocyanine
作者:Laibing Wang, Jun Li, Weidong Zhang, Gaojian Chen, Wei Zhang, Xiulin Zhu
关键字:http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2014/PY/c3py01129a#!divAbstract
论文来源:期刊
具体来源:Polym. Chem., 2014,5, 2872-2879
发表时间:2014年
Benzenedinitrile, a
precursor for the synthesis of phthalocyanine, was incorporated into a
methacrylate monomer, 2-methyl-acrylic acid
6-(3,4-dicyano-phenoxy)-hexyl ester (MADCE). The benzenedinitrile
monomer was homo-polymerized, chain-extended and copolymerized with
oligo(ethylene glycol) methyl methacrylate (OEGMEMA) via the
reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) method. The
resulting homopolymer, block and random copolymers obtained were used to
synthesize polymers with Zn(II)phthalocyanine (ZnPc)
side-chains by reacting with excess benzenedinitrile derivatives,
4-(octyloxy)phthalonitrile (OPN). GPC, FTIR, UV-Vis, NMR, fluorescence,
and atomic absorption spectroscopy were used to characterize the Zn(II)phthalocyanine-functionalized
polymers. The ZnPc-functionalized polymers generate singlet oxygen
species with good quantum yields, which are believed to be the major
cytotoxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) for photodynamic therapy. Among
them, copolymers present enhanced singlet oxygen quantum yields (ΦΔ= 0.49 and 0.40 in DMF, ΦΔ= 0.68 and 0.73 in aqueous media) compared to the homopolymer (ΦΔ= 0.28). The ZnPc-functionalized copolymers self-assembled into
nanoparticles in aqueous solutions, which was confirmed by DLS and TEM,
and the nanoparticles show good stability in the presence of salt and
proteins. This novel and efficient method of synthesizing water-soluble
ZnPc-functionalized polymers with good singlet oxygen quantum yields
provides a simple approach to fabricate polymeric materials for
photodynamic therapy.