- 热烈祝贺Engineered Science Publisher旗下Engineered Science期刊第1期论文正式上线
- 来源:顾军渭教授个人网站 2018-05-01
2018年年初在美国建立了工程科学出版社(http://www.espublisher.com/),同步创建了旗下的第一个综合性期刊Engineered Science,目前第1期论文已正式上线http://www.espublisher.com/journal/1101.html (Read this journal/Current Issue)。
本刊第二期论文也将于五月底出刊,然后8月(9月期)和11月(12月期)出刊,回归正常出版程序。此外,Engineered Science旗下的两个子刊(ES Energy & Environments,ES Materials & Manufacturing)近期也将上线,敬请各位专家学者多投稿、审稿,多浏览、下载和引用本出版社及旗下期刊论文,也敬请您多提宝贵意见,以便我们后期进一步优化和改进本出版社服务和旗下期刊质量,感谢您的大力支持!
Introducing Engineered Science
Hongbo Gu, Dapeng Cao, Jie Kong, Junwei Gu,Qinglong Jiang, Ying Li, Bin Wang, Xingru Yan, Yuan Chen, Jong Eun Ryu, Matthew Hu, Yajun Yan, Zhanhu Guo, Brian J. Edwards, David P. Young
Engineered Science, 2018, 1: 1-3
DOI: 10.30919/es.8d128
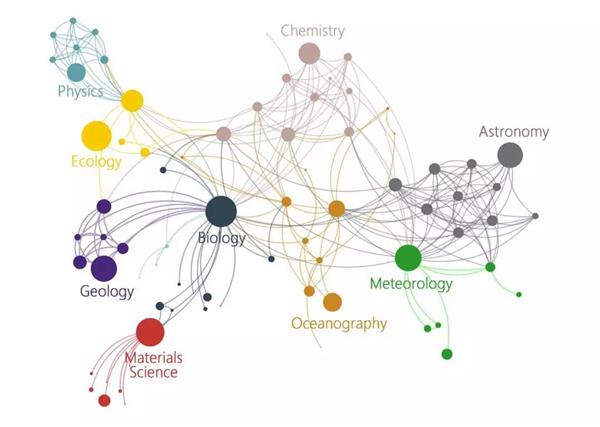
Human beings have struggled for thousands of years to understand the natural world. Throughout history, Science, the body of accumulated knowledge for testable explanations and predictions with regard to the physical and natural world, has driven the development and progress of human society. Science covers many multidisciplinary fields such as including physics, chemistry, biology, astronomy, geology, oceanography, ecology, meteorology, and many more, as shown in Figure 1. Mankind applies such broad branches of knowledge to advance human development and explore the unknown world. Science guides people in exploring the very large, such as the stars and the universe, in understanding the very small, such as subatomic particles and molecules, and in improving the human condition with advances in medicine and materials science.
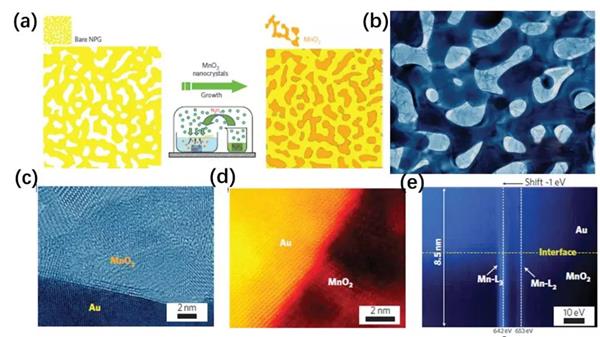
Electrodes with high conductivities for high performance lithium/sodium ion batteries
Litao Yan, Haizhen Wang, Di Huang, Hongmei Luo
Engineered Science, 2018, 1: 4-20
DOI: 10.30919/es.180318
Electrochemical devices including lithium/sodium-ion batteries and supercapacitors, as the promising solution to energy storage and environmental issues in the future, have attracted great attention recently due to the rapidly growing demand for non-renewable resources. The common electrode materials, including metal oxides, suffer from low conductivities, which lead to low charge transfer rate during the charge/discharge process and thus poor battery performance such as low specific capacitance/capacity, low rate capability, and poor cycling stability. Therefore, researchers have been searching for various strategies to enhance the conductivity of the electrode materials and thus the performance of lithium/sodium-ion batteries and supercapacitors. In this mini-review, different strategies to enhance the conductivities of the electrode materials would be discussed which will provide researchers various routes to improve the conductivity of the electrode materials in order to improve the performance of electrochemical device.
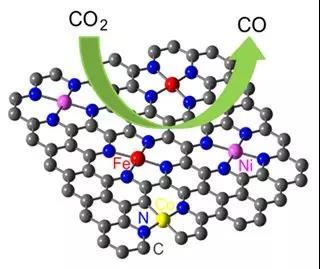
Nitrogen Coordinated Single Atomic Metals Supported on Nanocarbons: A New Frontier in Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction
Fuping Pan, Xianmei Xiang, Ying Li
Engineered Science, 2018, 1: 21-32
DOI: 10.30919/es.1804232
The rising level of atmospheric CO2 caused by increased fossil energy consumption is linked to global warming effects. Electrochemical CO2 reduction (CO2RR) can convert CO2 into value-added chemical fuels by using renewable energy-generated electricity as the energy input, providing a promising solution to mitigate the CO2 emissions. Compared to conventional precious metal catalysts for CO2RR, carbon-based catalysts are made of earth-abundant elements and less expensive, with great potential for large-scale applications. In this Review, recent advances of designing and synthesizing nitrogen coordinated single atomic transition metals supported on nanocarbons (M-NX-C; M=Fe, Ni, Co) as electrocatalysts for CO2RR are reviewed from both experimental and computational aspects. The catalytic mechanisms and design principles are highlighted, and the correlations of catalyst synthesis-structure-performance relationships are discussed. The disparities in catalytic activity between noble metal catalysts (Ag and Au) and M-NX-C catalysts suggest that there is still much room to develop more advanced M?NX-C catalysts. Therefore, several strategies, including mechanism exploration, M-NX sites and carbon supports engineering, and large-scale fabrication of atomically dispersed catalysts and reactor systems design are proposed to propel the use of M-NX-C for achieving high-efficient and costeffective CO2-to-fuels conversion.
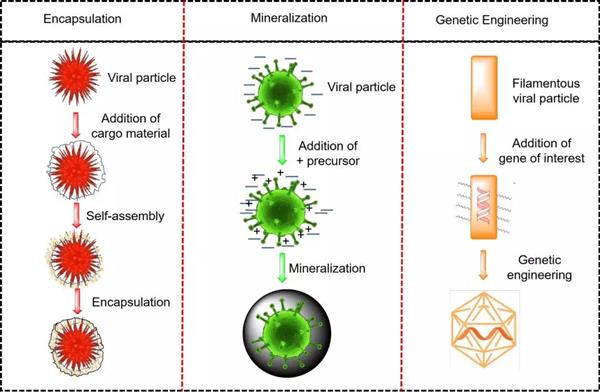
Surface engineering of microbial cells: Strategies and applications
Sabella Jelimo Kiprono, Muhammad Wajid Ullah, Guang Yang
Engineered Science, 2018, 1: 33-45
DOI: 10.30919/es.180330
Microbial cells (bacteria, fungi, and algae) and viruses are important part of life; which besides their harmful effects, perform several useful functions owing to their unique cell surface properties. The unique structures present on their surfaces serve as barriers between the cell and its environment and bestow them with unique functional properties. The current review describes strategies to decorate microbial cells by using different materials. It details various strategies such as layer by layer (LbL) decoration, mineralization, encapsulation, and genetic engineering among others to modify the surfaces of different microbial cells for potential applications such as environmental biotechnology, toxicology, medical microbiology, and nano-biotechnology, etc. Besides, it discusses the effects of various materials on cell viability, physiology, and functionality used for surface engineering. This review provides fundamentals to the novice readers and insights to the seasoned researchers to pave way for their future research in the area.
Chitosan-coated-magnetite with Covalently Grafted Polystyrene Based Carbon Nanocomposites for Hexavalent Chromium Adsorption
Hongbo Gu, Xiaojiang Xu, Hongyuan Zhang, Chaobo Liang, Han Lou, Chao Ma, Yujie Li, Zhanhu Guo, Junwei Gu
Engineered Science, 2018, 1: 46-54
DOI: 10.30919/espub.es.180308
A chitosan-coated-magnetite with covalently grafted polystyrene (g-PS) based magnetic carbon nanocomposites composed of carbon coated magnetite nanoparticles with carbonized g-PS microsphere are prepared for effective hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) adsorption. The adsorption measurements have indicated that the fabricated magnetic nanocomposites FC515 exhibit an effective Cr(VI) adsorption performance and the optimal pH for Cr(VI) adsorption on FC515 is 3.0 at 298 K. The Cr(VI) adsorption kinetics on FC515 is found to follow the pseudo-second-order behavior with a room temperature initial adsorption rate of 7.106 g mg-1 min-1 for the solution with an initial Cr(VI) concentration of 6.5 mg L-1 and pH value of 3.0. The adsorption isotherm test illustrates that the Langmuir isotherm model with a monolayer adsorption is well fitted for Cr(VI) adsorption on FC515 than the Freundlich isotherm model. The thermodynamic parameters including negative standard Gibb''''''''s free energy change and standard enthalpy change suggest that the Cr(VI) adsorption on FC515 is spontaneous and exothermic. After 5 cycles, FC515 still maintain 86% of Cr(VI) adsorption capacity, exhibiting a good reusability in practice. The zeta-potential and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements demonstrate that the Cr(VI) adsorption on FC515 is mainly from the electrostatic interaction between FC515 and Cr(VI). This work provides a new method to design the novel structure of magnetic carbon nanocomposites with natural polymer chitosan and thermoplastic PS for Cr(VI) wastewater treatment.
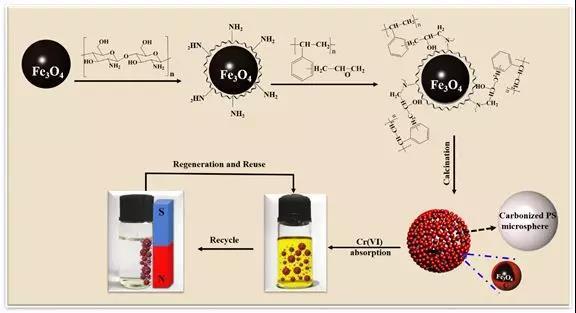
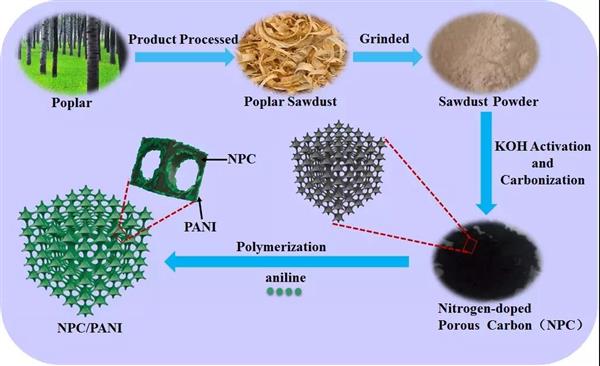
Biomass-derived nitrogen-doped porous carbons (NPC) and NPC/polyaniline composites as high performance supercapacitor materials
Xizhi Wang, Xiaofei Zeng and Dapeng Cao
Engineered Science, 2018, 1: 55-63
DOI: 10.30919/es.180325
Currently, developing high performance supercapacitor material suitable for application in the areas which require high energy density battery, is still a great challenge. Here we use biomass poplar sawdust as precursors to prepare nitrogen-doped porous carbons (NPC) and the NPC/polyaniline (PANI) composites, and further explore its application in supercapacitor electrodes. By optimizing the carbonization temperature, we find the NPC-750 sample shows a highest specific capacitance of 362 F·g-1 in 6 M KOH at 0.5 A·g-1 among the four samples, due to its large specific surface area of 2149 m2·g-1, and suitable pore size distribution and high graphitization degree. Further investigations indicate that NPC/PANI composite exhibits a much higher specific capacitance of 312 F?g-1 than 252 F·g-1of NPC at 5 A·g-1, and a wider voltage range of 0-1.4 V than the one of 0-1V of NPC, as well as a much higher energy density of 15.45 Wh·kg-1, which is 2.73 times of 5.66 Wh·kg-1 of NPC. This work indicates that integrating porous carbon and PANI into a composite is a promising strategy for developing high performance supercapacitor electrode materials.
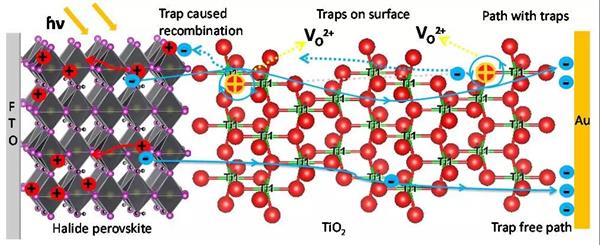
Nano-mesoporous TiO2 Vacancies Modification for Halide Perovskite Solar Cells
Qinglong Jiang, Liang Wang, Chao Yan, Chuntai Liu, Zhanhu Guo and Ning Wang
Engineered Science, 2018, 1: 64-68
DOI: 10.30919/es.180329
The efficiency of charge transport at interfaces and bulk affects the performance for lots optoelectronic devices. In this work, vacancies in nano-mesoporous TiO2 have been modified by hydrogen peroxide and the corresponding photoactive electrode for halide perovskite solar cells shows remarkable improvement of current density (Jsc) 36% and open circuit voltage (Voc) 10%, with overall improvement of efficiency over 75%. Photovoltage decay indicates the electron lifetime have been almost doubled after hydrogen peroxide treatment.
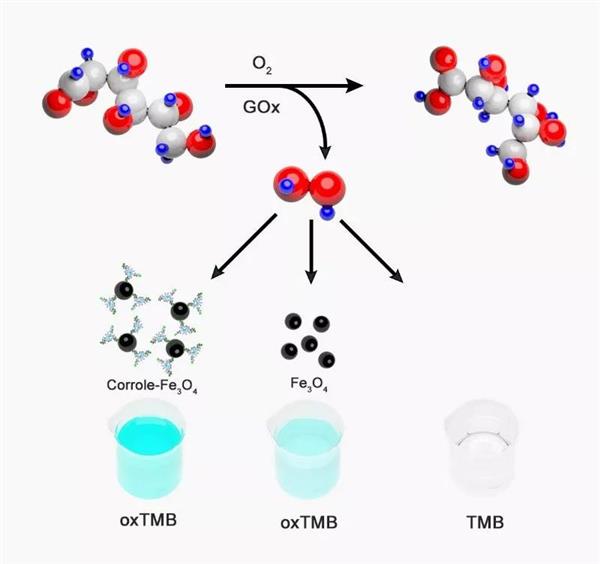
Corrole functionalized iron oxide nanocomposites as enhanced peroxidase mimic and their application in H2O2 and glucose colorimetric sensing
Linna Gao, Leyou Zhang, Xintian Lyu,Guifen Lu and Qingyun Liu
Engineered Science, 2018, 1: 69-77
DOI: 10.30919/espub.es.180314
For the first time, functional Corrole molecules modified iron oxide (Fe3O4) magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) were prepared by a facile two-step method. The Corrole-Fe3O4nanocomposites exhibited a higher peroxidase-like activity than that of pure Fe3O4 nanoparticles, and accelerated the oxidation of peroxidase substrate 3,3''5,5''-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) with the help of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) only in 5 min, attributing to hydroxyl radicals (OH) generated in the process of oxidation of TMB. Kinetic analysis showed that the catalytic behaviors followed the typical Michaelis-Menten kinetics. Additionally, Corrole-Fe3O4 exhibits several advantages including low cost, easy separation, facile fabrication, and high catalytic efficiency. Based on the catalytic activity of Corrole-Fe3O4nanocomposites, a simple, sensitive, and selective colorimetric biosensor for H2O2 and glucose determination was successfully designed. The linear relationships of absorbance of oxidized TMB at 652 nm with H2O2 or glucose concentration were obtained from 10 μM to 100 μM with a detection limit of 3.6 μM and 4 μM to 40 μM with the detection limit as low as 2.46 μM, respectively. The results demonstrate that the Corrole-Fe3O4nanocomposites have potential applications in bioanalysis and biodetection.
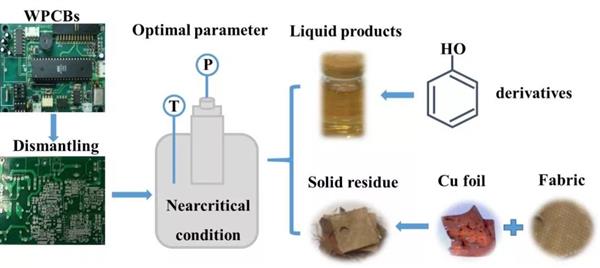
Separation and Recovery of Copper Foil and Fabric from Waste Printed Circuit Boards by Decomposing Brominated Epoxy Resin Using Near Critical Water
Hongjun Kang, Qian Shao, Xingkui Guo, Alexandra Galaska, Yuyan Liu, Zhanhu Guo
Engineered Science, 2018, 1: 78-85
DOI: 10.30919/espub.es.180312
Waste printed circuit board (WPCB), a heterogeneous mixture of brominated epoxy resins (BERs), glass fibers and metals, has the challenge to separate and recover valuable materials. In this paper, an effective and benign near critical water (NCW) method was applied to decompose BERs to recover the glass fabric and metals. The effects of parameters including temperature, reaction time, feed ratio, acid-base catalyst, and size of WPCBs on the decomposition ratio of BERs were investigated. The results showed that the decomposition ratio of BERs reached a maximum value of 98.7% under the optimum conditions at 320 °C, reaction time of 150 min, feed ratio of 5 mL/g, HCl catalyst, and the size of 5×5 mm2. The gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC/MS) result showed that the main components of liquid decomposition product were phenol (69.8%) and its derivatives (17.8%). A probable mechanism of the decomposition reaction of BERs was proposed. After NCW treatment, the glass fabric and copper foils in the residue were easily recovered by a simple artificial screening separation. The surface of recovered fabric was very clean and no damages were observed. Meanwhile, the purity of copper foil reached 97.86%. This study provides a green technology to recover valuable materials from WPCBs.
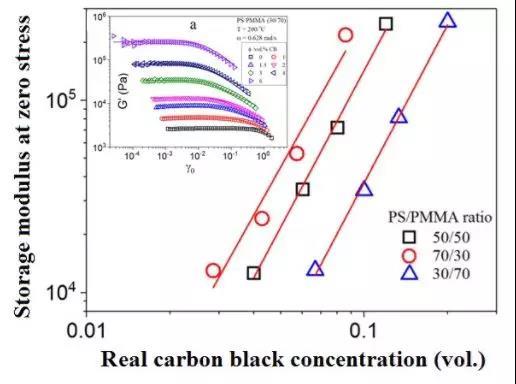
Dynamic oscillatory rheological properties of polystyrene/poly(methyl methacrylate) blends and their composites in the presence of carbon black
Yamin Pan, Dirk W. Schubert, Jong Eun Ryu, Evan Wujick,Chuntai Liu,Changyu Shen,Xianhu Liu
Engineered Science, 2018, 1: 86-94
DOI: 10.30919/es.180402
In this work, the polystyrene/poly(methyl methacrylate) ((PS/PMMA) blends and their composites with different PS/PMMA ratios and different carbon black (CB) contents were prepared by melt mixing. The rheological properties of immiscible PS/PMMA blends and PS/PMMA/CB composites are deeply discussed to understand the relationship between the rheological properties and the CB particle network. For the blends with a sea-island morphology, a shoulder is observed at low-frequency region due to the shape relaxation of dispersed droplets. However, for the blends with a co-continuous morphology, the frequency sweep exhibits power-law dependences with a small terminal slope. As the CB concentration increases, the slope of storage moduli versus angular frequency plots in the low angular frequencies becomes much lower than 1. This suggests that the composite exhibits a transformation from liquid-like to solid-like states. Moreover, a linear relationship between the storage moduli at zero stress and the CB concentration in the PS phase (real CB concentration) is proposed regardless of the PS/PMMA ratio.
- [来源:中国聚合物网]
- 了解更多请进入: 顾军渭教授个人网站